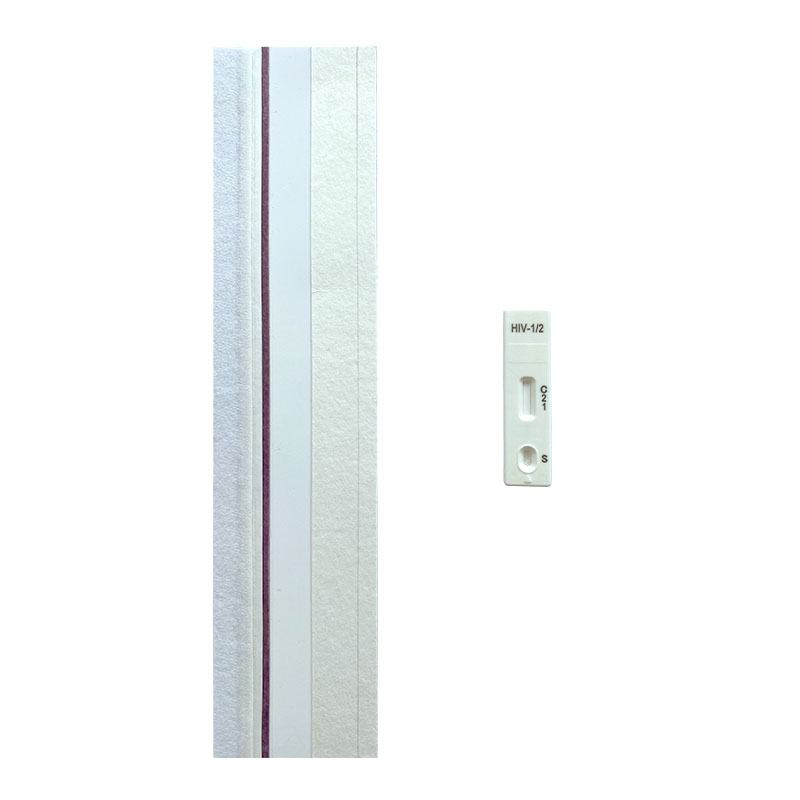
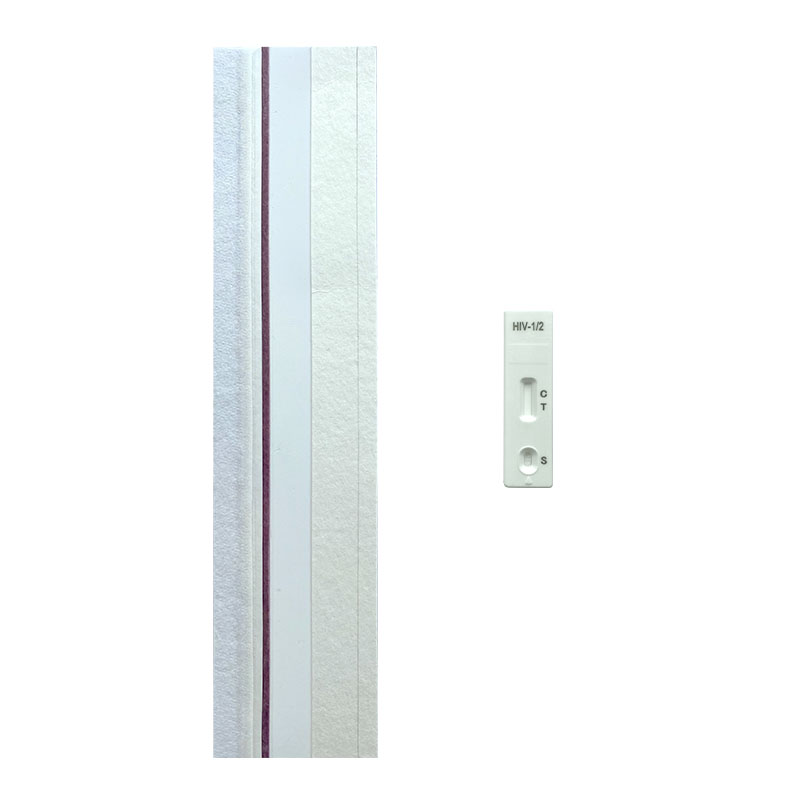
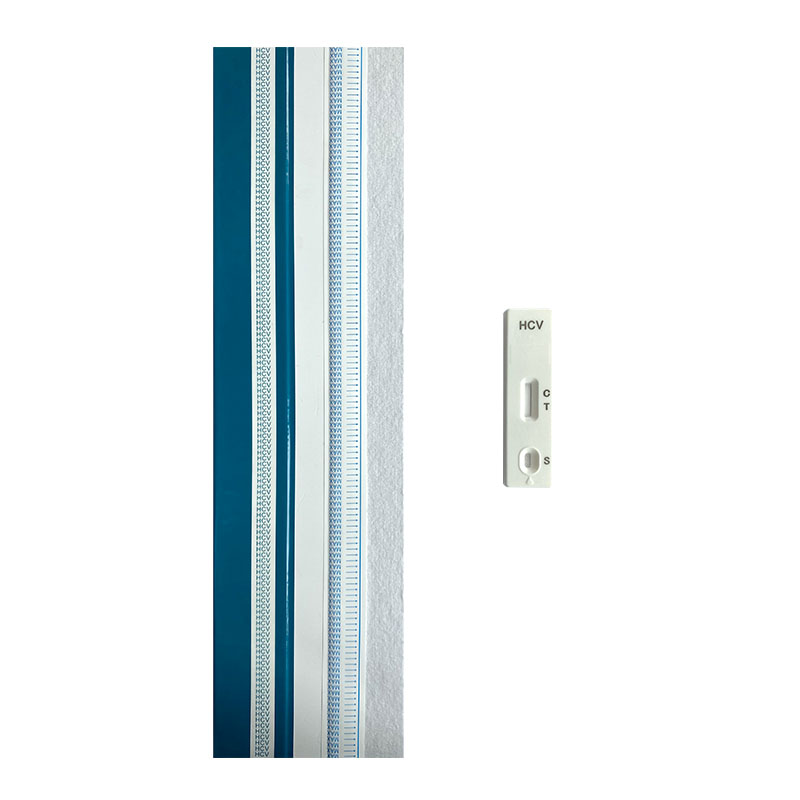
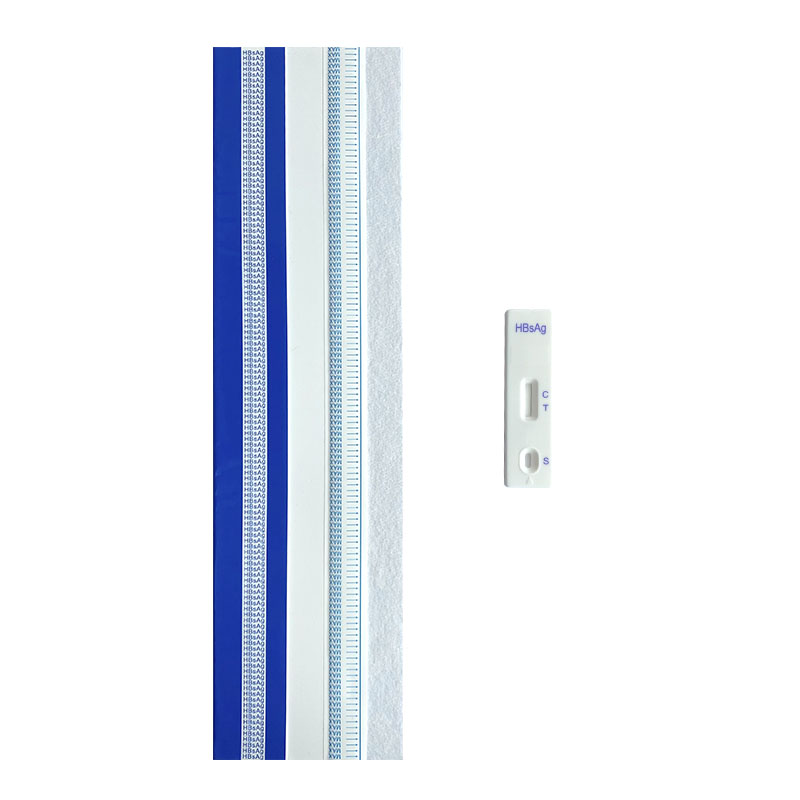
Infectious Disease Test Uncut Sheet
NewScen provides a comprehensive range of Infectious Disease lateral flow rapid test kits, ensuring swift and accurate detection of various infections including HIV 1/2, HCV, HBsAg, HBsAb, HEV, TP, TB, HAV, HPAb, HPAg, ADENOVIRUS (Ag), NORO (Ag), ROTA (Ag), TYPHOID (Ag), TYPHOID (IgG/IgM), HSV (IgG), RSV (Ag), STREP A (Ag), and CHLAMYDIA (Ag).
We offer uncut sheets for all our products, allowing for flexible customization and scalability. Trust NewScen for reliable and efficient infectious disease testing solutions.
List of Other Available Disease Test Uncut Sheet
NewScen provides rapid diagnostic test uncut sheets for all our produced lateral flow assays. If the specific uncut sheet you require is not listed, please don’t hesitate to contact us for more details.
| UNCUT SHEET | PRODUCT DESCRIPTION |
| ADENOVIRUS (Ag) | Adenovirus Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| NORO (Ag) | Norovirus (NORO) Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| ROTA (Ag) | Rotavirus (ROTA) Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| TYPHOID (Ag) | Typhoid Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| TYPHOID (IgG/IgM) | Typhoid IgG/IgM Antiobdy Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| HSV (IgG) | Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV Type II) IgG Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| RSV (Ag) | Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| STREP A (Ag) | Group A Strep Tococcal Antigen (STREP A) Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
| STREP B | Strep B Rapid Test Uucut Sheet |
| CHLAMYDIA (Ag) | Chlamydia Antigen Rapid Test Kit Uncut Sheet |
Understanding Our Target Audience



Please feel free to contact us immediately to request samples for your Uncut Sheet business before commencing the rapid test production.
FAQ
Testing for infectious diseases typically involves several approaches depending on the specific disease and its characteristics. Here are some common methods used in infectious disease testing:
1.Molecular Tests: These tests detect the presence of the pathogen's genetic material (DNA or RNA) in a patient's sample. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a widely used molecular technique that amplifies the genetic material, making it easier to detect.
2.Serological Tests: These tests detect the presence of specific antibodies produced by the immune system in response to an infection. Blood samples are collected and analyzed to identify the antibodies, indicating whether the person has been exposed to the pathogen.
3.Antigen Tests: Antigen tests detect the presence of specific proteins from the pathogen in a patient's sample. These tests are often used for rapid diagnosis as they provide quick results, typically within minutes.
4.Culture Tests: In this method, a sample from the patient is collected and cultured in a laboratory to isolate and grow the pathogen. This allows for further identification and characterization of the infectious agent.
5.Imaging Techniques: Imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can be used to visualize and identify certain infectious diseases, particularly those affecting the respiratory or gastrointestinal systems.
It is important to note that the choice of testing method depends on various factors, including the suspected infectious agent, the stage of infection, the availability of resources, and the purpose of the test (diagnosis, screening, or surveillance). Healthcare professionals and laboratories follow specific guidelines and protocols to determine the most appropriate testing approach for each infectious disease.
Laboratory tests for infectious diseases include molecular tests (such as PCR), serological tests (detecting antibodies), antigen tests, and culture tests.
There is no single "best" test for infection as it depends on the specific infection being targeted and the purpose of the test. Different tests, such as molecular tests (PCR), serological tests, antigen tests, or culture tests, may be more suitable depending on the circumstances.
The colloidal gold antigen test, also known as a lateral flow assay or rapid antigen test, is a diagnostic test used to detect the presence of specific antigens in a patient's sample. The principle of this test is based on the immunochromatographic technique. Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:
1. Sample Collection: A sample, such as a nasal swab or saliva, is collected from the patient suspected of having an infectious disease.
2. Sample Preparation: The collected sample is typically mixed with a buffer solution to prepare it for testing.
3. Test Strip: The test strip consists of several components arranged in a specific order:
a. Sample Pad: The sample, along with the buffer solution, is applied to this pad, which helps control the flow of the sample.
b. Conjugate Pad: This pad contains colloidal gold nanoparticles that are coated with antibodies specific to the target antigen. These antibodies are designed to bind with the target antigen if it is present in the sample.
c. Nitrocellulose Membrane: The membrane is coated with a control line and a test line. These lines contain immobilized antibodies that are specific to the target antigen. The test line antibodies are the same as those on the colloidal gold particles, while the control line antibodies are specific to a different molecule that should always be present in the sample.
d. Absorbent Pad: This pad acts as a wicking material, drawing the sample along the test strip through capillary action.
4. Test Process:
a. The prepared sample is applied to the sample pad of the test strip.
b. The sample flows along the strip, carrying any target antigens present in the sample.
c. As the sample reaches the conjugate pad, the colloidal gold nanoparticles bind to the target antigens, forming antigen-antibody complexes.
d. The complex continues to flow along the strip and reaches the test line area.
e. If the target antigen is present in the sample, the antigen-antibody complex binds to the antibodies on the test line, resulting in the formation of a visible line.
f. Any excess colloidal gold particles that are not bound to the target antigen continue to flow and reach the control line area, where they bind to the control line antibodies, forming another visible line.
5. Result Interpretation: The appearance of both the test line and control line indicates a valid test. The intensity of the test line can provide information about the concentration of the target antigen in the sample. If the test line does not appear, it suggests that the target antigen is not present in the sample.
The colloidal gold antigen test offers a rapid and convenient method for detecting specific antigens, making it useful in point-of-care settings and for mass screening purposes.
The colloidal gold device for HIV is a diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of HIV antibodies in a patient's blood or saliva sample. It is based on the principle of lateral flow immunoassay, where colloidal gold nanoparticles are conjugated with HIV-specific antibodies. When the sample is applied to the device, if HIV antibodies are present in the sample, they bind to the colloidal gold conjugates. This interaction results in the appearance of a visible test line on the device, indicating a positive result for HIV infection. The colloidal gold device provides a rapid and simple method for HIV screening and can be used in various healthcare settings.









