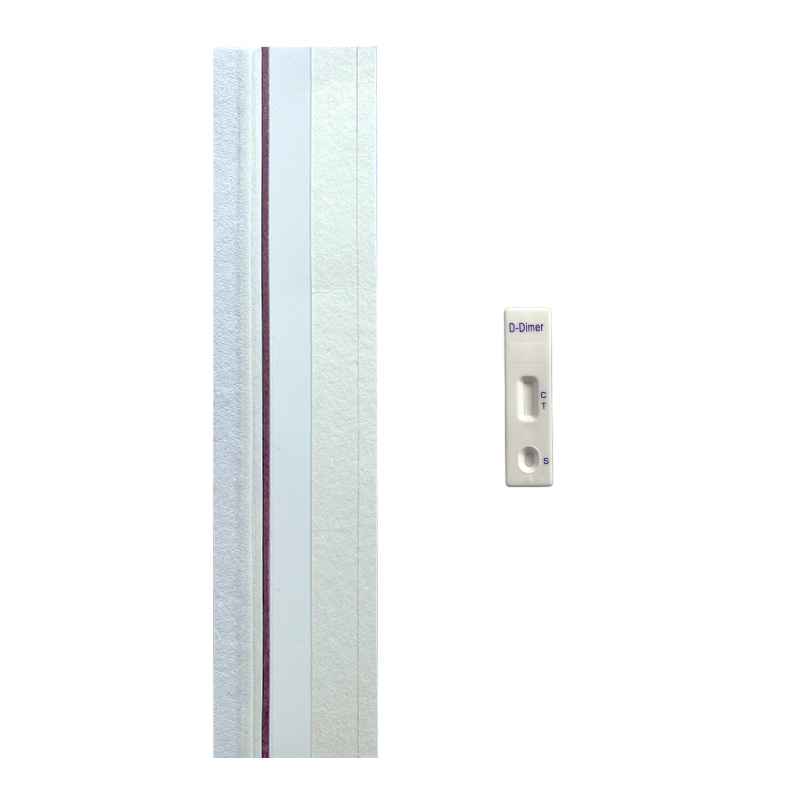
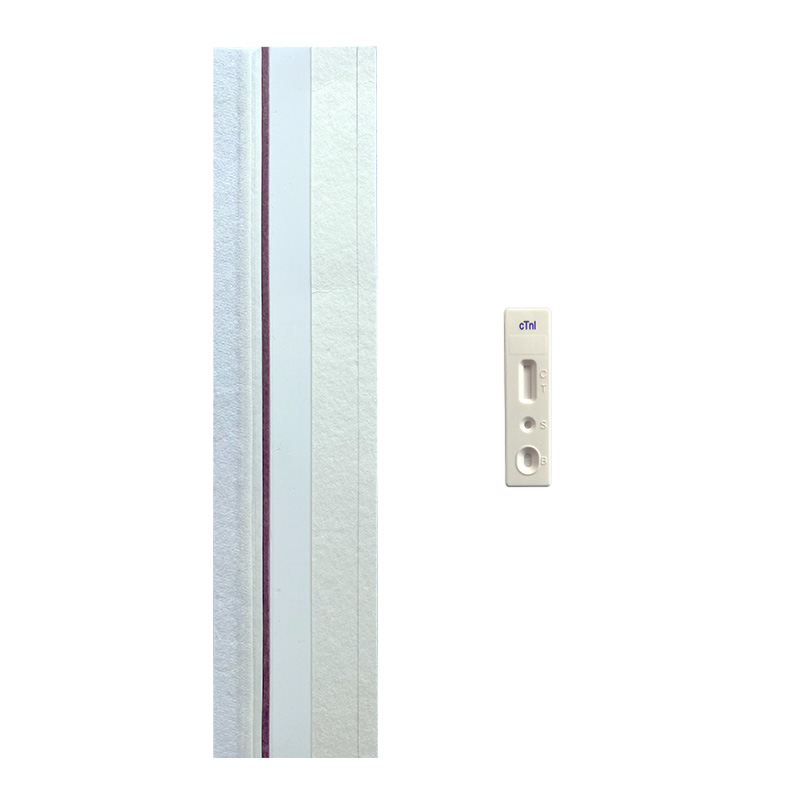
Cardiac Marker Test Uncut Sheet
NewScen provides a comprehensive range of Cardiac Marker lateral flow rapid test kits, ensuring swift and accurate detection of various infections including D-Dimer, cTnI.
We offer uncut sheets for all our products, allowing for flexible customization and scalability. Trust NewScen for reliable and efficient Cardiac Marker testing solutions.
List of Other Available Cardiac Marker Test Uncut Sheet
NewScen provides rapid diagnostic test uncut sheets for all our produced lateral flow assays. If the specific uncut sheet you require is not listed, please don’t hesitate to contact us for more details.
Understanding Our Target Audience



Please feel free to contact us immediately to request samples for your Uncut Sheet business before commencing the rapid test production.
FAQ
cTnT is a different protein than cTnI and actual mass concentrations in blood are generally much lower (5-10 fold than those of cTnI. Therefore, the numerical result from a cTnT assay cannot be directly compared to a cTnI result. As mentioned previously, both cTnI and cTnT are cardiac specific with one rare exception.
Cardiac markers are substances released into the bloodstream in response to damage or stress to the heart muscle. They are used to diagnose and monitor various cardiac conditions, including myocardial infarction (heart attack). Enzymes play a crucial role as cardiac markers, indicating heart muscle injury. The primary enzymes used as cardiac markers are:
Creatine Kinase (CK): CK is an enzyme found in the heart, brain, and skeletal muscles. Elevated levels of CK-MB (isoform specific to the heart) in the blood suggest myocardial damage.
Troponin: Troponin is a protein complex found in cardiac muscle cells. Troponin I (cTnI) and Troponin T (cTnT) are released into the bloodstream when heart muscle is injured. Troponin levels are highly specific to cardiac damage and are considered the gold standard for diagnosing myocardial infarction.
Myoglobin: Myoglobin is a protein found in heart and skeletal muscle. It is released rapidly after muscle injury, including myocardial infarction. However, it is not specific to the heart, limiting its diagnostic utility.
These enzymes are measured using blood tests to evaluate the presence and severity of cardiac injury. They help healthcare professionals make timely and accurate diagnoses and determine appropriate treatment strategies for patients with cardiac conditions.
Troponin is a good cardiac marker because it is a protein found exclusively in heart muscle cells. When heart muscle is damaged, such as during a heart attack, troponin is released into the bloodstream. Measuring troponin levels allows for the early and accurate detection of myocardial injury, providing critical information for diagnosing and managing cardiac conditions. Its high specificity and sensitivity make troponin a reliable indicator of cardiac damage and an essential tool in evaluating and monitoring patients with suspected or known heart disease.
Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and troponin I (cTnI) are cardiac regulatory proteins that control the calcium mediated interaction between actin and myosin. The cardiac forms of these regulatory proteins are coded by specific genes and theoretically have the potential of being unique to the myocardium.
Troponin rise from a MI occurs due to cardiac injury from acute cardiac ischaemia, although elevated levels are also seen in acute or chronic conditions not recognized as classical MI. This is often referred to as a 'false positive' rise, which is not entirely true as there is some underlying cardiac injury.

